Hydrogen bromide (HBr) is a polar molecule because of the electronegativity difference between Hydrogen (2.2) and Bromine (2.96). Bromine is higher electronegative than hydrogen so it attracts electron from hydrogen, as a result, two dipole poles are induced therefore the molecule has a net dipole moment.
Detailed Explanation: Why is HBr a Polar Molecule?
HBr whose chemical name is hydrogen bromide and its aqueous solution is known as hydrobromic acid, is a colorless to light yellow liquid which
is formed by one atom of hydrogen and one atom of bromine and considered a strong
acid.
Polar Molecules
Polar molecules are simply defined as the presence of a polar bond
within the molecule or have irregular geometry (not symmetrical structure), so the net dipole moment of the molecule is not zero as the center of gravity of negative
charge and positive charge is separated by a small distance.
These molecules are used to show little ionic
characteristics i.e. they are soluble in water, can conduct electricity, have
strong electrostatic force and many more.
Examples of Polar molecules: Water (H2O), Hydrochloric acid(HCl), Ammonia (NH3), etc.
Nonpolar Molecules
Nonpolar molecules are simply pure covalent bonded molecules
with mutual sharing of electrons and have net dipole moment zero. As there are
no occurrence of partial positive and negative charge on the atoms because of the same electronegativity difference between the atoms (Diatomic molecules like H2,
O2, N2, etc) or molecule has regular geometry (symmetrical molecules like CCl4,
CO2 etc) so bond polarities are canceled by each other.
When Nonpolar molecules are placed in an electric field, the
center of gravity of positive charge moves in direction of the field, and the center of the gravity of negative charge in opposite direction. This separation between
positive and negative charges continues until the applied external force and
internal force are balanced.
Example of Nonpolar molecules: All diatomic molecules (H2,
N2, O2, Cl2, etc.), Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4), Carbon Dioxide (CO2), Xenon tetrafluoride (XeF4) etc.
HBr Polar or Nonpolar (On the basis of characteristics)
Hydrogen bromide (HBr) is a polar molecule and the Bromine
atom closest to the negative side because bromine has a higher electronegativity
than hydrogen atom so that Bromine pulls the lone pair of electrons slightly
closer which causes induction of positive charge on H atom and negative charge on
Br atom.
Electronegativity Difference
Electronegativity is a kind of force exerted by an atom or
molecule at the time of bond formation on the binding partner. It means an atom
exerts a force on the corresponding bonding atom at the time of the sharing of a lone
pair of electrons. The higher the electronegative value, the more force will be exerted
for attracting the electrons. If two atoms having the same EN value exerted forces
will be canceled out.
In the HBr molecule,
Electronegativity of Hydrogen= 2.2
Electronegativity of Bromine= 2.96
Electronegativity difference= 2.96-2.2= 0.76
From the above data, the electronegativity difference between H and Br is about 0.76 and according to the Pauli scale, if the electronegativity difference between two atoms is between 0.5 to 2.0, the corresponding bond is considered as polar bond. Thus, the EN difference is 0.76, the H-Br bond is polar.
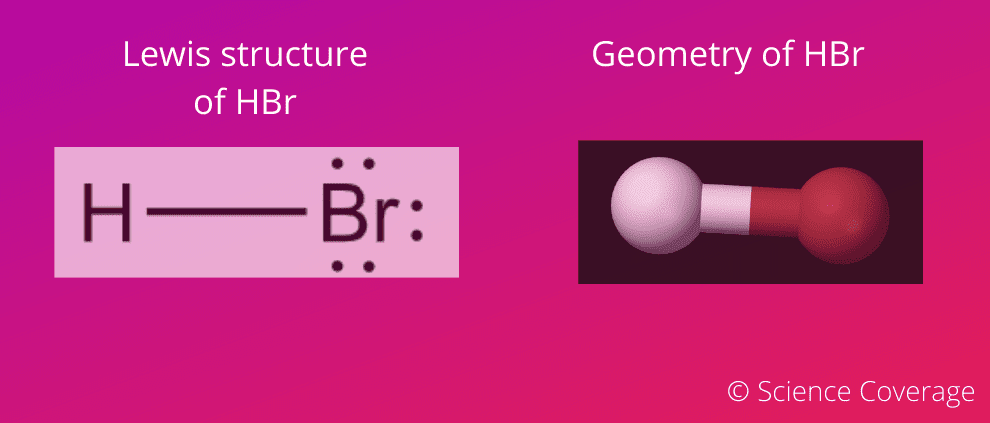
Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
HBr compound has a total of 8 valence electrons (electrons
on the outermost shell), one from hydrogen and 7 from bromine which takes part
in the formation of the Lewis dot structure. Both atoms share one lone electron to
fulfill their outermost shell at the time of bonding.
Dipole Moment
The dipole moment is a major asset for any compound being polar or nonpolar. Those molecules having net dipole moment zero are considered as nonpolar molecules and the rest are polar. Dipole moment can be defined as the products of induced charge and distance of separation. It is denoted by and given by,
Dipole moment = Charge (Q) * distance of separation (r)
It is measure in Debye units denoted by ‘D’. 1D = 3.33564*10-30 C.m, where C is Coulomb and m denotes a meter.
Hydrogen bromide has a net dipole moment of 820 mD which arises
due to the difference in electronegativity between the hydrogen and bromine and
also, the geometry of the molecule is linear.
Electron Affinity
Electron affinity is the possibility of finding an electron at
the orbit of an atom or molecule. It is impossible to determine the exact
position of an electron at a particular time according to the uncertainty
principle. But we can just predict the maximum chances of getting an electron
according to the nature of the molecule or atom.
As HBr is a polar molecule, the maximum chances of getting an
electron is higher closer to the bromine atom because it pulls the lone pair of
electrons closer to its nucleus. But in the nonpolar molecules, the maximum chances of
getting an electron is higher at the central position of the bond.
Solubility Principle
According to the solubility principle “likes dissolve likes” means
polar compounds are soluble in different polar solvents and nonpolar solvents
are soluble in nonpolar solvents. Same in the case of HBr, it is soluble in water
which is a polar solvent to produce hydrobromic acid. Not only in water it can
easily be soluble in many more polar solvents like alcohol, ammonia, etc.
Sources and preparation of Hydrogen bromide (HBr)
For industrial purposes, Hydrogen bromide is prepared by combining hydrogen and bromine at a temperature of 400 °C in the presence of a platinum catalyst.
In the laboratory, it is most commonly prepared by distillation
of potassium bromide with sulfuric acid.
KBr + H2SO4 → KHSO4 + HBr
Properties of HBr
1. It is a colorless gas with a pungent irritating odor and has
a molecular mass of 80.91 g/mol.
2. It is highly corrosive and irritating to inhalation so that
it should be handled very carefully otherwise causes many serious problems.
Uses of HBr (Hydrobromic acid)
- It is used in many chemical intermediate products as sanitizing and disinfecting agent.
- Used in the preparation of many organic compounds as a reagent and catalyst.
- It is also used in a utility-scale flow-type battery.

Post a Comment